Author: Rosemin Anderson
Subject Matter Expert: Topher Mitchell
What is customer behavior analysis?
Customer behavior analysis involves the systematic examination of your customers’ actions, both habitual patterns and unique interactions, concerning your business. It leverages both quantitative data and qualitative data to scrutinize current customer behavior and develop informed predictions about future trends. This process allows businesses to proactively take steps to refine and improve the overall customer experience.
The ways customers shop, the frequency of their purchases, their responses to marketing campaigns, and their commentary about your brand on social media platforms all represent valuable customer data points for analysis. Successfully understanding customer behavior and the underlying motivations enables you to adapt your strategies across products or services, sales, and marketing efforts. This alignment helps foster the desired customer behavior patterns. Delivering a customer experience that genuinely meets customer needs increases the likelihood of driving favorable actions and boosting sales, while simultaneously optimizing operational costs. A deep dive into customer behavior analysis is fundamental for this.
Free eBook: Moving your customer experience metrics forward
Why understanding customer behavior is crucial for business success
Grasping the intricacies of customer behavior is not merely an interesting exercise; it’s a cornerstone of sustainable business growth and enhanced customer satisfaction. Effective customer behavior analysis provides the foundation for strategic decision-making, impacting everything from product development to customer service protocols. When businesses invest in analyzing customer behavior, they gain a competitive edge by anticipating market shifts and customer needs more accurately.
This understanding allows companies to move beyond reactive measures, enabling them to proactively shape the customer journey. By identifying what truly motivates customers and addressing potential friction points, businesses can cultivate stronger customer relationships, foster brand loyalty, and ultimately improve their bottom line. The insights derived from customer behavior analysis empower organizations to allocate resources more effectively, focusing efforts where they will yield the greatest impact on customer satisfaction and business results. Understanding consumer behavior directly translates to smarter business strategies.
How extensive can customer data analysis be?
Customer data analysis, as part of a broader customer behavior analysis strategy, can provide a comprehensive view of your customer base, revealing insights at both an aggregate and individual level. It helps uncover the reality behind customer actions, as customers don’t always behave in the ways they articulate. Analyzing customer behavior through data allows businesses to understand what truly happens during brand interactions.
By examining a combination of customer-generated data (gathered through observation, tracking, and analysis of actions) and operational data (such as financial records, customer demographics, employee information, and product ownership details), businesses can employ qualitative and quantitative approaches. This dual approach helps identify how customers behave at each touchpoint along the customer journey and illuminates the drivers behind that behavior. Utilizing sophisticated customer behavior analysis tools can significantly aid in surfacing trends and actionable insights from vast amounts of customer data, turning raw information into strategic intelligence. This level of data analysis is crucial for understanding the complete customer experience.
Why is customer behavior analytics important for businesses?
Understanding how your customers behave and the reasons behind their actions might initially seem like a secondary concern, but why is customer behavior analytics fundamental to achieving business results and ensuring high customer satisfaction? The importance lies in its ability to transform raw customer data into strategic advantages.
Identifying patterns helps you make accurate predictions for the future
Developing a strong grasp of customer behavior trends allows you to discern patterns in how customers shop, utilize your services, or engage with your brand. Are there specific times, seasons, or periods when customers are more likely to purchase? Which marketing campaigns or value propositions resonate most effectively and drive purchasing behavior? Critically, at which stage of the customer journey do customers tend to churn, and what specific interventions could encourage them to stay? Analyzing customer behavior helps answer these vital questions.
Research indicates a significant expectation from customers; for instance, Salesforce found that 63% of B2C consumers and 76% of B2B customers anticipate brands will understand their unique needs and expectations. By meticulously analyzing behavior patterns through robust customer behavior analysis, you can design and deliver interactions that not only meet but exceed these expectations. This alignment drives business value by providing your target audience precisely what they seek, fostering positive customer relationships and encouraging repeat business. Identifying patterns is a core benefit of customer behavior analytics.
Drilling down on existing customer behavior helps you win over new customers
Conducting thorough customer behavioral analysis offers insights that extend beyond your current customer base; it equips you to attract and convert new customers more effectively. The deeper understanding gained allows for precise customer segmentation based on behavioral trends rather than just demographics. This enables more targeted marketing efforts.
According to data from Invesp, the probability of selling to an existing customer ranges from 60-70%, whereas the likelihood of converting a new customer is considerably lower, at 5-20%. The more comprehensively you understand each segment within your existing customer base, the better you can predict the likely behavior patterns of similar new customers. This predictive capability allows you to tailor the initial customer journey for maximum impact.
Furthermore, by identifying the specific behaviors characteristic of your high value customers, you can predict which prospective customers are likely to follow similar patterns. This foresight enables you to proactively deliver an optimized customer journey designed to nurture these potentially loyal customers from their very first interaction, maximizing customer lifetime value. Understanding existing customers through customer behavior analysis is key to acquiring new ones.
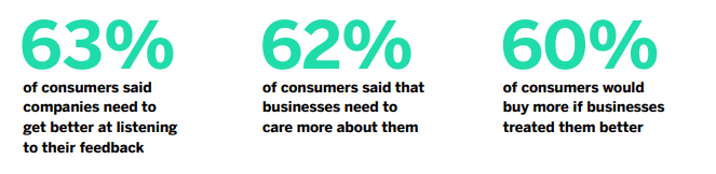
Personalizing customer experiences drive sales
Your business constantly receives streams of relevant customer data. Customers are often willing to communicate their desires, preferences, and experiences, whether positive or negative. Leveraging customer feedback and other forms of customer data to tailor the customer experience is a powerful strategy for shaping customer behavior proactively.
Our own research into global consumer trends highlights this point: two-thirds of customers believe companies need to improve their listening skills regarding feedback, and 62% feel brands should demonstrate greater care for them and their customer preferences. Significantly, 60% of surveyed customers indicated they would purchase more from a brand if they felt genuinely cared for. This underscores the commercial impact of personalization derived from understanding consumer behavior.
Personalizing experiences effectively can substantially improve business value. With the right data analysis techniques, taking into account both observed behavior and direct feedback, you can implement personalization at scale. Crafting bespoke customer journeys that align with natural customer behavior removes friction points and optimizes the entire process. This, in turn, significantly increases the probability of higher conversion rates and improved business results, demonstrating the power of actionable insights from customer behavior analysis. Tailoring marketing messages based on this analysis is crucial.
Understanding behavior helps you to increase customer retention
Why do certain customers remain loyal to your brand over time? Are specific negative experiences, such as encountering broken website links or technical glitches during the customer journey, driving customers away or reducing their engagement? Conversely, what specific actions or experiences solidify their decision to stay and continue engaging with your products or services? Effective customer retention strategies hinge on answering these questions.
Analyzing customer behavior is instrumental in identifying these critical pain points and informing the development of the most effective solutions. By understanding the nuances of customer interactions and preferences, you can optimize the customer journey accordingly. This proactive approach helps reduce customer churn by minimizing frustration and removing reasons for customers to seek alternatives. Addressing issues identified through customer behavior analysis directly impacts customer loyalty.
Considering that a significant portion of business revenue, often cited as high as 65%, typically comes from the existing customer base, ignoring the valuable insights derived from customer behavior analysis is a risk few businesses can afford. Focusing on customer retention through behavioral understanding is essential for long-term success and maximizing customer lifetime value.
See how understanding customer behavior can improve the experience in real time
Key types of customer behavior data
To conduct a meaningful customer behavior analysis, it’s essential to gather and interpret different forms of customer data. This data broadly falls into two categories: qualitative and quantitative. Both provide unique perspectives on customer actions and motivations, and combining them offers a more holistic understanding of consumer behavior. Utilizing both qualitative and quantitative data is fundamental to comprehensive data analysis.
Qualitative data
Qualitative data provides context and understanding behind the numbers. It delves into the ‘why’ of customer behavior, capturing subjective experiences, opinions, and feelings. Key sources include direct customer feedback gathered through surveys, interviews, or focus groups. Analyzing open-ended responses can reveal deep customer behavior insights into satisfaction levels, unmet needs, and specific pain points within the customer journey.
Conversation analytics, derived from customer service interactions (calls, chats, emails), offers another rich vein of qualitative data. Tools employing natural language processing can analyze text and speech to identify customer sentiment, intent (e.g., seeking information, making a purchase, lodging a complaint), and perceived effort. Understanding the emotional tone and effort involved in interactions provides crucial context for interpreting customer behavior patterns and improving the customer experience. Qualitative data helps understand the nuances of customer satisfaction.
Quantitative data
Quantitative data consists of measurable, numerical information that describes ‘what’ customers are doing. This type of customer behavior data is often easier to collect at scale and analyze statistically to identify broad trends and patterns. Examples include purchase history, which reveals buying frequency, average order value, and product/service popularity among different customer segments. Analyzing transactional data is key here.
Website and app analytics provide quantitative data on user behavior online, such as page views, time spent on site, click-through rates, bounce rates, and conversion paths. Social media engagement metrics (likes, shares, comments, follower growth) quantify how customers interact with your brand on these platforms. Furthermore, tracking customer service metrics like the number of support tickets raised, resolution times, and first-contact resolution rates offers quantitative insights into operational efficiency and potential friction points impacting customer satisfaction and overall customer behavior. Quantitative data provides scale to customer behavior analysis.
How do you perform a customer behavior analysis?
You recognize the value in identifying and understanding customer actions, but what are the practical steps involved in finding, analyzing, and acting upon these insights? Performing a robust customer behavior analysis is an ongoing process, not a one-time task.
Here’s a structured guide to help you implement effective customer behavior analysis:
1. Define your customer segments
While you likely have existing buyer personas, revisiting and refining your customer segments is a crucial first step before diving into consumer behavior analysis. Segmentation should go beyond basic demographics to capture deeper behavioral and psychographic attributes relevant to how customers interact with your brand.
Consider segmenting based on:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income, location, family status, education level. (Note: While useful for context, demographics are often less predictive of specific customer behavior than other factors).
- Psychographics: Hobbies, interests, lifestyle, values, beliefs, aspirations (personal and professional).
- Professional information: Industry, job title, company size (especially relevant for B2B).
- Needs and challenges: Pain points, problems they are trying to solve, specific needs your product/service addresses.
- Product/service usage: How they use your offering, frequency of use, features utilized, their reliance on your brand.
- Engagement profile: Preferred communication channels, social media activity, potential influence within their networks.
- Barriers and motivations: Objections to purchase, external factors influencing buying decisions (e.g., budget constraints, competitor actions), company-related issues hindering purchase (e.g., price, usability), key drivers for purchase.
Ideally, focus on identifying the characteristics of your most valuable customer segments – those exhibiting high customer lifetime value and strong brand loyalty. Key factors to analyze within segments include:
- Customer satisfaction: Which segments report the highest satisfaction? What factors do they cite as key drivers of their positive experience?
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Which customer segments demonstrate the highest long-term value through repeat purchases and sustained engagement? Calculating and segmenting by CLV is a powerful way to prioritize efforts and understand which customer behavior patterns contribute most significantly to revenue. Identifying high value customers is crucial.
Refining customer segments based on these factors provides a clearer picture of your target audience and helps focus your subsequent data analysis efforts. Effective customer segmentation is foundational.
2. Gather qualitative and quantitative data on customer behavior
With clearly defined customer segments, particularly focusing on high-value groups, the next step is to systematically gather relevant customer behavior data. As discussed, this involves collecting both quantitative data (the ‘what’) and qualitative data (the ‘why’).
Sources for quantitative data are numerous and often trackable through existing systems:
- Transactional data: Purchase history, order frequency, average order value, product/service combinations frequently bought together.
- Website/app analytics: Traffic sources, page views, session duration, bounce rates, conversion funnels, clickstream data, feature usage within apps. Platforms like Qualtrics for Strategy & Research can capture, analyze, and report on digital behavior in seconds or minutes instead of days or weeks.
- Social media metrics: Engagement rates (likes, shares, comments), follower growth, mentions, sentiment analysis (often requires specialized tools).
- Marketing campaign data: Email open/click-through rates, ad conversion rates, landing page performance.
- Customer service data: Number of support tickets, resolution times, first-call resolution rates, channel usage (phone, chat, email).
Sources for qualitative data often require more direct interaction or sophisticated analysis tools:
- Direct customer feedback: Surveys (NPS, CSAT, CES, open-text questions), interviews, focus groups. Qualtrics’ Digital Experience Analytics (DXA) solution excels at collecting and analyzing this type of feedback across the customer journey.
- Conversation analytics: Analysis of call recordings, chat transcripts, and email interactions to identify sentiment, intent, effort, and emerging themes using tools that leverage AI and natural language processing.
- Review sites & social listening: Monitoring online reviews (e.g., G2, Capterra, Google Reviews) and social media conversations for unsolicited feedback and opinions about your brand, products, or services.
- Usability testing: Observing users interacting with your website or product to identify pain points and gather direct feedback on the user experience.
Gathering comprehensive qualitative and quantitative data across multiple touchpoints provides the raw material needed to build a rich understanding of user behavior and purchasing habits. Utilizing customer behavior analysis tools that integrate these diverse data sources can streamline this process and enhance the depth of your analysis, helping you understand the entire customer journey. Ensuring data security throughout this process is paramount.
3. Evaluate your data for behavior insights
Once you have collected a robust set of customer data across your defined segments, the critical phase of evaluation begins. This involves analyzing the information to identify meaningful patterns, trends, and correlations that reveal insights into customer behavior. Simply collecting data isn’t enough; the goal is to transform it into actionable intelligence. This often requires dedicated data analysis skills and potentially powerful customer behavior analytics tools, especially when dealing with large datasets.
What are the 4 types of customer buying behavior?
Understanding common frameworks for classifying consumer behavior can help structure your data analysis. While individual behavior is complex, recognizing typical patterns can provide valuable context. Your collected data might align with some of these established types of customer buying behavior and theoretical approaches:
- Extended decision-making: Characterizes high-involvement purchases (often expensive or infrequent). Customers invest significant time and effort in research, comparing alternatives, reading reviews, seeking recommendations, and evaluating options before making a purchase decision. Analyzing the research paths and information sources used during this process is key.
- Limited decision-making: Occurs for purchases where the customer has some prior experience but may still evaluate a few options. The search is less extensive than extended decision-making, perhaps involving checking prices or looking for specific features. Availability or convenience can play a larger role.
- Habitual buying behavior: Describes low-involvement, frequent purchases where customers exhibit little brand differentiation seeking. They often buy out of habit or familiarity, with minimal conscious decision-making (e.g., buying the same brand of milk). Understanding what reinforces this habit is important for customer retention.
- Variety-seeking buying behavior: Seen in low-involvement categories where customers perceive significant brand differences and enjoy experimenting. They might switch brands frequently out of curiosity or boredom, rather than dissatisfaction. Understanding the drivers for switching is crucial for marketing messages.
What are the five consumer behavior approaches?
- The Economic Man Approach: Assumes customers make rational decisions based primarily on price and utility, aiming to maximize value with limited resources.
- The Cognitive Approach: Views consumers as information processors who go through distinct mental stages: need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase evaluation. Understanding bottlenecks in this process is vital.
- The Psychodynamic Approach: Draws on Freudian concepts, suggesting behavior is driven by unconscious motives and the desire to resolve internal conflicts (e.g., balancing desires with societal norms).
- The Behaviorist Approach: Posits that behavior is learned through stimulus-response conditioning. Past experiences (positive or negative reinforcement) shape future actions. Brand loyalty can be seen through this lens.
- The Humanistic Approach: Emphasizes individual uniqueness, self-interest, and subjective experiences as drivers of behavior. Purchases are seen as expressions of individuality.
Identify patterns
Using your collected qualitative and quantitative data, look for recurring themes and behavior patterns across your customer segments. Ask targeted questions to guide your data analysis:
- How do different customer segments typically discover and first interact with your brand (e.g., search engines, social media, email marketing, referrals)?
- Are there specific times (day, week, month, season) when purchasing activity peaks for certain segments or products?
- What are the common points of friction or abandonment during the purchase process (e.g., complex checkout, unexpected costs, technical issues)? What specific issues prevent customers from completing desired actions?
- Conversely, what actions or features correlate strongly with higher engagement, conversion, or usage (e.g., completing profile setup quickly, using a specific feature)?
- Which website design elements, navigation paths, or platform functionalities cause frustration or confusion for users? Session replay tools can offer valuable insights here.
- Which marketing campaigns, messages, or channels have demonstrably influenced purchasing behavior or engagement for specific segments?
- What factors encourage repeat purchases and contribute to building loyal customers? Is it product quality, customer service, loyalty programs, or personalized communication?
- What underlying emotions, needs, or motivations (identified through qualitative data) seem to precede significant purchase decisions?
- How much effort do customers perceive they need to exert to interact with your brand or complete a purchase? Reducing effort often improves customer satisfaction.
Employing customer behavior analytics tools, particularly those offered by platforms like Qualtrics, can automate much of the pattern identification process. These tools can analyze vast datasets, surface statistically significant trends, identify drivers of key metrics (like satisfaction or churn), and even use predictive analytics to forecast future behavior based on current patterns. This allows you to move from simply analyzing data to gaining deeper insights.
Discover the truth of customer experience
A critical aspect of evaluating customer behavior data is reconciling what customers say with what they actually do. Self-reported preferences or intentions gathered through surveys (qualitative data) don’t always align perfectly with observed actions tracked through analytics (quantitative data). For instance, a customer segment might state a preference for engaging via social media, but transactional data might reveal that email marketing campaigns are far more effective at driving their actual purchases.
Effective consumer behavior analysis requires acknowledging and investigating these potential discrepancies. The “truth” often lies in the synthesis of both qualitative and quantitative data. Understanding why these differences exist (e.g., aspirational reporting vs. actual convenience-driven behavior) provides valuable insights for optimizing the customer journey map and crafting more effective marketing strategies. Focus on the actionable insights derived from the convergence (or divergence) of these data types.
4. Adjust your customer journey and experience for better customer lifetime value
The primary goal of customer behavior analysis is not just understanding, but action. Once you have analyzed your data and extracted meaningful customer behavior insights, the final step is to apply this knowledge to optimize the customer experience and refine the customer journey map. This involves making strategic adjustments designed to minimize undesirable behaviors (like cart abandonment, high bounce rates, unresolved customer service issues) and encourage desirable ones (like repeat purchases, increased engagement, positive reviews, higher purchase frequency). This is an ongoing process of refinement.
This often requires modifying aspects of your products or services, marketing messages, sales processes, or customer support protocols. For example:
- Product Bundling: If data analysis reveals that customers frequently purchase two specific products together, consider creating a bundle offer. This anticipates customer needs, simplifies the purchasing process, reduces effort, and can potentially increase average order value.
- Proactive Communication: If analysis shows that new users of a service app often fail to add payment details within the first day, leading to later friction, implement a targeted reminder email or in-app prompt shortly after download to encourage this crucial step. This addresses a specific behavioral bottleneck identified through analyzing customer behavior.
- Website/App Optimization: If session replays and analytics indicate users struggle with a particular part of your website navigation or checkout process, redesign that element for improved clarity and ease of use. Addressing usability issues identified via customer behavior analysis directly impacts customer satisfaction.
- Personalized Marketing Campaigns: If certain customer segments respond particularly well to specific types of content or offers, tailor future marketing campaigns accordingly. Use behavioral segmentation to deliver more relevant marketing messages, increasing engagement and conversion rates. This leverages customer behavior insights for more effective marketing efforts.
- Customer Service Enhancements: If analysis highlights recurring issues or long resolution times reported through customer feedback and support tickets, invest in additional training, improved knowledge base resources, or streamlined support processes. Improving service based on customer behavior data enhances customer relationships.
Optimize your customer experience to better reflect customer behavior
Systematic customer behavior analysis provides invaluable intelligence for understanding and improving the entire customer journey, from the initial awareness and research stages through purchase, onboarding, usage, and post-purchase engagement or feedback. By understanding behavior patterns and implementing data-driven changes, you deliver an enhanced, more intuitive, and satisfying customer experience. The direct outcomes are increased customer loyalty, improved customer retention, boosted customer lifetime value, and often, a reduced cost to serve satisfied customers.
Solutions like Qualtrics® Customer Experience software offer comprehensive solutions that facilitate not only customer behavior analysis but also the subsequent actions needed to shape future customer interactions positively. By integrating data collection across touchpoints, providing powerful analytics for identifying patterns and drivers (including predictive analytics), and enabling targeted actions – from refining the customer journey map to launching hyper-personalized marketing campaigns – you can create an adaptive system. This ongoing process allows you to continually refine your understanding and predict customer behavior with increasing accuracy over time.
At the end of the day, your aim is to provide customers with a journey that consistently exceeds their expectations and meets their needs seamlessly, grounded in the valuable insights generated through rigorous customer behavior analysis.
This focus on understanding and responding to customer behavior is fundamental to building lasting customer relationships and achieving sustainable business success.
Free eBook: Moving your customer experience metrics forward