What is product research?
Product research is the process of gathering insights to develop, improve or successfully launch a product, service or experience.
It helps product teams and businesses make informed decisions at every stage of the product lifecycle, from exploring new ideas and testing concepts, to setting prices, tracking product-market fit after launch — and even evaluating packaging.
Whether you’re building something new or refining something already out there, when you conduct product research you’re working to reduce risk and increase your chances of success.
In practice, it combines qualitative and quantitative methods to collect data and answer key questions, such as:
- What does our target market need or want?
- How does this idea stack up against the existing competition?
- Will people buy this product — and at what price?
Although the name suggests a focus on physical products, product research applies just as much to services and experiences. It often works hand-in-hand with market research to help you align what you’re offering with what people truly value.
Done right, thorough product research is a powerful tool to guide strategy, optimize design and build products people love.
Why is product research crucial?
Even the most original, innovative, or disruptive product idea can fall flat if it doesn’t meet real customer needs. And if it doesn’t, it can never be considered a great product — no matter how strong the idea.
Whether you’re launching something new or improving an existing offer, product research helps you avoid guesswork and build something people actually want. It replaces assumptions with insights, so you can make smarter decisions at every stage of development.
Turn ideas into viable offerings
Product research helps you determine if your idea has real-world potential — what problems it solves, who it’s for, and what features or benefits people actually care about.
Make confident, evidence-based decisions
Product research helps you test early, iterate quickly and make decisions based on real customer insights — reducing risk and improving your chances of success.
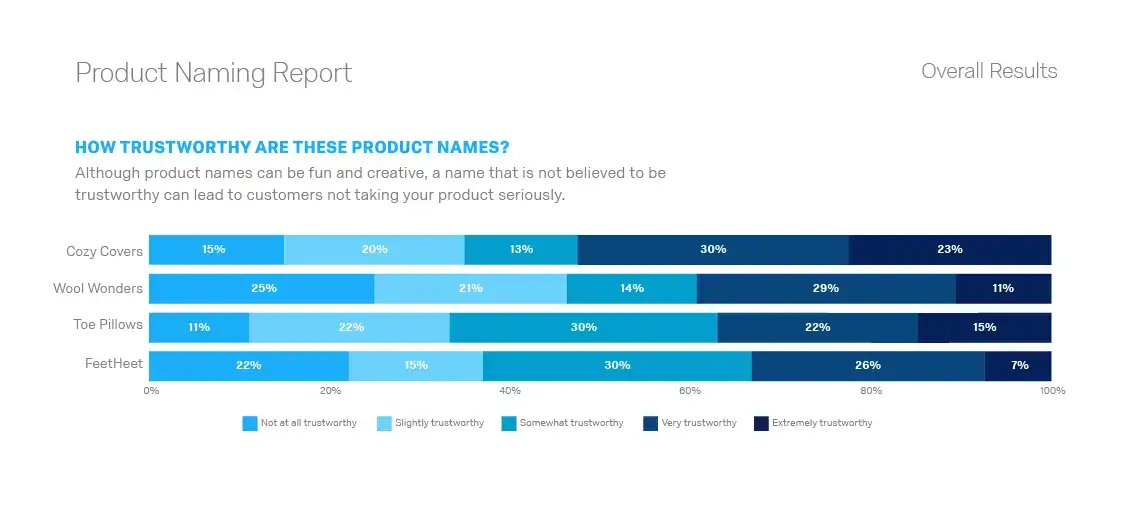
Align products with market demand and customer needs
Product research helps you understand the broader landscape — what your competitors are doing, what customers expect and where unmet needs lie — so you can create something that truly fits the market.
Kickstart your next product launch with our free, ready-to-use product research survey template
Core components of effective product research
Effective product research is built on three foundations: understanding the world your product will enter, the people you’re building it for and the product itself.
Let’s break each element down and explore the reasons why they’re so crucial.
Understanding your market and competitors
Before you build anything, you need to understand the context your product will exist in. Market and competitor research helps you identify where opportunities lie — and where others have already staked a claim.
Markets are constantly shifting
Staying on top of macro and micro trends in your space will help you avoid short-lived fads, time your launch effectively and align your offer with emerging demand.
Competitive gaps reveal opportunities
By knowing your competitors and identifying what they’re getting right — and where they’re falling short — you can position your product to fill a clear and compelling gap.
Positioning only works if it’s rooted in reality
Knowing the landscape and where you stand in it will help you define a value proposition that’s not only distinctive, but credible and commercially viable.
Understanding your customer
Great products solve real problems for real people. To build one, you need to understand your customers beyond surface-level demographics.
Different customers have different needs
Market segmentation will reveal which groups are most likely to benefit from your product — so you can prioritize the audiences that matter most.
Customer decisions are driven by emotion as much as logic
Understanding what motivates your users — and what frustrates them — will help you design experiences that connect on a deeper level.
Adoption demands alignment with real-world behavior
The better you understand how your target audience thinks, shops and uses products, the easier it is to create something that fits seamlessly into their lives.
Understanding and validating your product
Once you’ve mapped the market and understood your audience, you need to test whether your product truly delivers on its promise — and where it needs to improve.
Even strong ideas need validation
What seems obvious to a product team can fall flat with users. Research reduces the risk of investing in the wrong thing by grounding development in real feedback.
Usability issues often go unnoticed until it’s too late
Watching how users interact with your product can surface user experience (UX) challenges and friction points that surveys can’t catch — saving you costly fixes post-launch.
Iteration is key to staying relevant
With customer needs evolving, expectations changing and your competitors moving fast, your product can’t afford to stand still. Iteration is key to keeping customers engaged and attracting new ones, and ongoing product research ensures you’re improving in the right direction.
Product research methods
To build products that people actually want, you need more than instinct or opinion — you need insight. That insight comes from research, and more specifically, from using the right mix of research methods at the right time.
Product research relies on a combination of quantitative and qualitative research to uncover what customers do, think and feel. Where quantitative methods help you spot patterns and validate decisions with data, qualitative methods help you understand the meaning behind the numbers — giving you context, nuance and emotion.
Quantitative methods: Validate and measure at scale
Measuring demand, tracking behavior and testing different solutions with statistical confidence, quantitative methods can help you understand what’s happening at scale.
Here are three of the most common and effective quantitative methods in product research.
Surveys
Surveys allow you to collect structured feedback from a large sample of your target audience with ease — particularly when conducted online. They’re ideal for testing concepts, ranking feature preferences, validating willingness to pay or tracking satisfaction over time.
When designed well, surveys can help you prioritize your product development based on what matters most to customers — aligning your product roadmap with actual demand and improving your chances of success in market.
Web and product analytics
Built-in analytics tools can track what users do inside your product or on your site, quantifying behaviors through heatmaps, user journeys, drop-off points and more.
This real-world, often real-time behavioral data reveals which features are performing well, where users are struggling, and how they navigate your product. With these insights, teams can prioritize the most impactful improvements and make decisions grounded in user behavior.
A/B testing
A/B testing compares two or more versions of a feature, layout or message to see which performs better.
Whether you’re testing pricing, onboarding flows, UX copy or homepage design, the results can help you make changes backed by evidence — not gut feel.
A/B testing is considered a fast, reliable way to improve conversion rates, increase engagement and maximize return on investment (ROI) over time.
Qualitative methods: Explore motivations and meaning
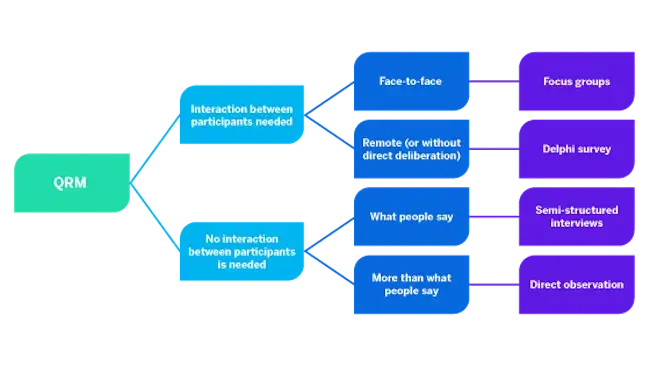
Qualitative methods help you get closer to your customers — revealing how they think, what they value and why they make the choices they do.
These insights are crucial in the early stages of product development in particular, when you’re identifying unmet needs, shaping ideas and testing assumptions.
User interviews
User interviews allow you to explore how people experience a problem or product in their own words.
By surfacing pain points, expectations and behaviors, interviews help you uncover what really matters to users. This leads to more relevant feature prioritization, clearer positioning and a stronger product-market fit — reducing the risk of building something no one needs.
Focus groups
Focus groups bring together a small group of target customers to discuss their views on a product, feature or concept.
The group setting encourages discussion and debate, often revealing shared attitudes and emotional reactions that can shape both design and messaging. Focus groups are useful for refining your value proposition and identifying potential objections before launch.
User testing
User testing can reveal usability issues that might otherwise go unnoticed. Whether the user hesitates, gets stuck or misinterprets an element of your prototype or live product, their experience can generate a goldmine of insights — helping you determine what needs to be improved and how.
Addressing these pain points early can help reduce customer frustration and churn, while improving adoption — ultimately driving customer retention and customer satisfaction.
Key product research applications
From shaping early ideas to refining features and pricing strategies, product research is applied at various different stages in the product development process for different purposes.
Here are three of the most important ways research supports effective product development:
Idea generation: Uncover opportunities worth building
Before a product even exists, research can help surface promising product ideas that are grounded in real customer needs by revealing unmet needs and opportunities for innovation.
This type of exploratory research fuels product discovery and ensures you’re solving the right problems — before jumping into solutions. Here, combining qualitative insight with audience segmentation or trend analysis can also help prioritize which customer problems are worth solving from a market opportunity perspective.
Research platforms like Qualtrics® XM™ for Strategy & Research can now streamline this process with tools for segmenting user feedback, identifying emerging needs and visualizing opportunity areas across audience groups.
Get fast, actionable feedback on your product ideas — download our free survey template now
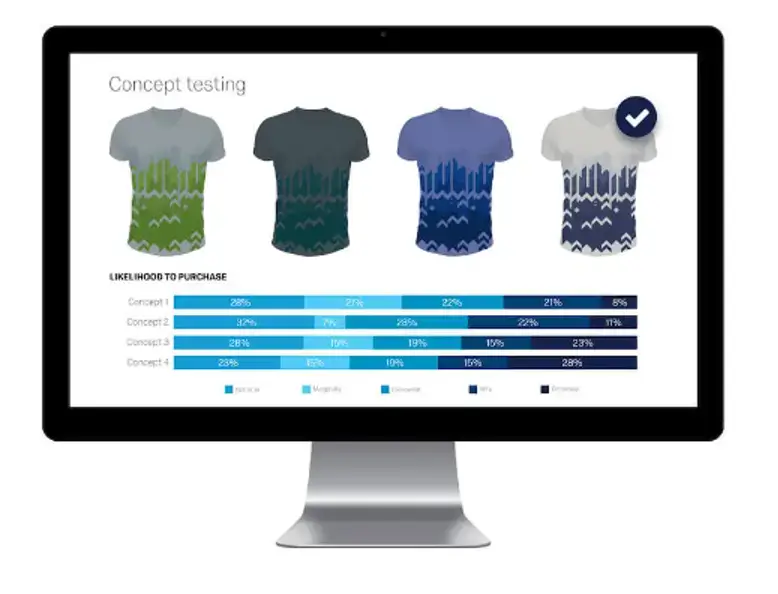
Concept testing: Validate ideas before investment
Concept testing is essential for refining ideas, de-risking development and assessing product-market fit. It helps you evaluate how potential customers respond to early concepts, prototypes or MVPs — before major investment is made.
Agile concept testing can be done in short cycles throughout the innovation process, using surveys to assess reactions to value propositions, designs, features or naming. Product research tools like Qualtrics also offer customizable templates and dashboards to rapidly capture and analyze user feedback across different segments.
By identifying what works — and what doesn’t — early on, concept testing reduces wasted spend and helps align your product with genuine market demand.
Pricing research: Find the optimal price point
Setting the right price is a balancing act between value perception and profitability — and getting it wrong can have major consequences.
This is why pricing research is crucial. It helps you understand what customers are willing to pay, what signals value, and how different pricing options impact demand and positioning.
Depending on your goals, you can apply a range of pricing research methods, such as:
- Van Westendorp’s price sensitivity meter, which gauges price acceptability by asking customers what’s too cheap, too expensive and just right
- Gabor-Granger pricing methodology, which asks users if they would purchase at different price points to identify maximum willingness to pay
- Conjoint analysis, which measures how users value different feature-price combinations and what trade-offs they’re willing to make
These approaches are often built into survey tools that support dynamic pricing simulations and segmentation analysis — helping you model revenue impact across audiences and confidently set pricing that your target audience can get onboard with.

Implementing an ongoing product research strategy
Product research doesn’t end at launch — it evolves with your product. Teams that achieve product research success work on a continuous loop: learning from every interaction, making targeted improvements and feeding those insights back into the development cycle.
Here’s how to become one of them in three practical steps:
Step 1: Gather continuous feedback post-launch
While you may feel like it’s the end, launching your product is just the beginning. Once it’s out in the world, every user interaction becomes a potential transformative insight.
Whether it’s through in-app surveys, pop-ups after feature use or follow-up emails, lightweight feedback mechanisms have become highly popular tools for capturing reactions in context. You can also monitor satisfaction through CSAT or NPS, and collect open-text feedback at key touchpoints like cancellations or support interactions.
For example, an e-commerce brand might ask users why they abandoned checkout, or an app might prompt users for feedback after trying a new feature. These quick, low-friction touchpoints can give you a steady stream of input that can be immediately surfaced within your product team and beyond.
Step 2: Use insights to iterate and improve
You’ve got your insights; now is time to turn them into action.
Let’s say your onboarding flow has a 40 percent drop-off rate. Feedback reveals users don’t understand its value fast enough, so many drop off early. In response, you run a round of usability tests, tweak the onboarding copy and flow, A/B test the changes with new users and find a clear winner that’s eventually rolled out.
By collecting the data, interpreting it and then actioning it, you’ve course-corrected early and built a better product.
Over time, this kind of targeted, insight-led iteration can have a significant positive impact on usability, retention and even product-market fit.
Step 3: Close the loop from concept to in-market feedback
The final — and often overlooked — step is connecting your early-stage research with real-world performance.
Did your most promising concept in testing actually perform best once launched? Did the features your target customers said they wanted become the ones your existing customers actually use?
Linking pre-launch assumptions with post-launch data helps you validate your research, refine future product decisions, and improve how you scope and position ideas in the first place.
For example, if conjoint analysis suggested a specific price-feature combination was optimal, but conversion data tells a different story, you can revisit your assumptions and adjust. Likewise, if a value proposition that tested well but falls flat in live marketing, it’s a sign to refine your messaging.
This feedback loop helps ensure every cycle of product research gets sharper, faster and more accurate — giving you a sustainable edge over competitors.
Accelerating insights with an integrated platform
The most effective product teams don’t just collect insights — they act on them quickly, confidently and at scale. That’s where an integrated research platform makes all the difference.
The Qualtrics Product Research solution brings together everything you need to test, validate, and optimize your products — and all in one place. With powerful analytics and an intuitive interface, you can move faster from insight to action and build products that customers truly want.
Supercharge your product research process through:
- Customizable, agile surveys for concept testing, pricing and user feedback
- Real-time dashboards that visualize customer preferences and product performance
- Advanced analytics and segmentation to identify trends and target high-potential audiences
- Integrated feedback loops to iterate continuously post-launch
- AI-powered suggestions to guide product improvements based on real customer input
Whether you’re exploring a new idea or scaling an existing product, Qualtrics helps you reduce risk, improve product-market fit, and stay ahead of the competition.
Take a tour of Qualtrics Product Research today to see how you can power your next breakthrough.