What is behavioral segmentation?
Behavioral segmentation is one type of market segmentation within the field of behavioral marketing. This looks at exploring similarities between groups, audiences, prospects, and customers by their actions and behaviors. Where demographic and psychographic segmentation study who makes up your customer base, behavioral segmentation looks at what your customers do.
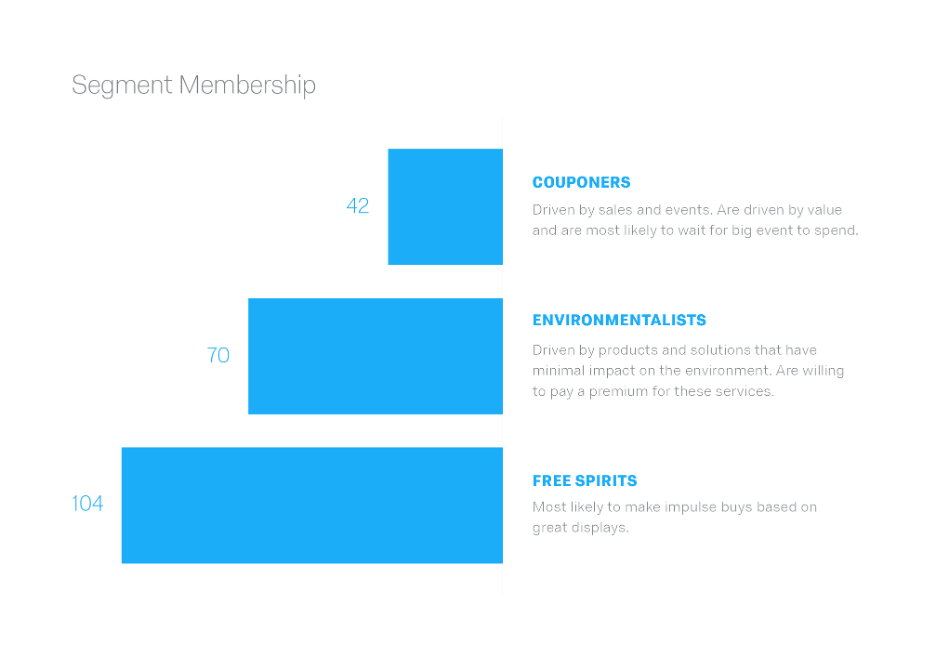
Customer behavior can be grouped together based on interactions with your brand, product, or service, such as:
- Customer attitudes toward it
- How customers use it
- Customers’ overall knowledge and awareness of it
- How customers buy it
In the world of ecommerce, behavioral segmentation can be carried out by examining online customer behavior:
- How long do they browse your website (dwell time)?
- How rapidly do they click off your site (bounce rate)?
- Are they new or returning customers?
- What do they add to their basket or playlist?
- How frequently do they abandon their cart?
Effective, data-informed behavioral segmentation has been made possible by the development of artificial intelligence. Powerful AI marketing analysis platforms can help deliver fast and accurate behavioral market segmentation. An all-in-one platform could, for example, collect behavioral data, create segment-based behavior graphics and help deliver tailored content reports for each consumer segment.
Benefits of behavioral segmentation
Why is behavioral segmentation a key driver of ROI for your marketing spend? Developing a deeper understanding of your loyal customers is about more than looking at customer data – it’s about making your outreach efforts more effective.
As an example, just using email marketing with messaging that’s targeted using behavioral segmentation can generate 58% of all revenue, whereas marketers using segmented campaigns for emails have noted a 760% increase in revenue.
Here are the main reasons why behavioral segmentation can prove to be worth the investment:
- Better targeting accuracy: You’ll be able to take advantage of different behaviors, and, knowing those, direct your marketing messages. For example, newer customers may be attracted to great introductory offers, while long-standing loyal customers may enjoy benefits from loyalty programs like an invitation to join an exclusive VIP club.
- More personal experiences: The days of blanket-bombing your email marketing lists with the same generic message are thankfully long gone. By identifying your audience’s needs, wants, concerns, and the type of messages they notice, you can connect with each one personally, making relevant offers and suggestions they are more likely to accept.
- Find higher customer engagement by filtering the interested from the uninterested: By separating the most engaged customers from the least, you can target your product or services at people who need or want them the most.
- Cost-effectiveness: You can target your budget at your most interested, engaged, and valuable audiences, rather than waste it on cold leads and the uninterested.
- Trackable: You can track metrics within each segment, take action and improve results.
- Increase customer loyalty: Customers who feel special will stick with the brand that makes them feel that way. Customer loyalty increases customer lifetime value, which translates to greater revenue for your business.
Free eBook: How to drive profits with customer segmentation
Why you should use behavioral segmentation alongside demographic and psychographic segmentation
There are different types of marketing segmentation to consider, and behavioral segmentation doesn’t happen in isolation. It works in partnership with demographic, psychographic, and
When using segmentation, marketers will often go for easy ways to divide customers. Demographic data is a simple way of grouping customers together with easy-to-source information, such as your average customer’s location, but it doesn’t provide the whole picture.
When examining your audience, psychographic data can help your brand understand the motivations behind customer behavior. What are the interests and lifestyle choices of your existing customers compared to new customers? Does their choice of activities influence your target audience’s decision to purchase with your brand? However, just because a customer is interested in your market doesn’t mean they’re going to buy.
Behavioral segmentation examines past behavior and applies insights to help predict future behavior. Historical behavioral patterns often influence new decisions, and keeping loyal customers happy often means giving them opportunities to repeat past behaviors that gave them satisfaction. Overlaying this information on the other data you have—who customers are, what they’re interested in—allows you to understand purchase drivers and estimate responses to your actions.
Where other segmentation data suggest potential interactions with your brand, behavioral Developing a holistic view of your customers through all these types of segmentation will yield valuable answers to how to target them most effectively. Used in conjunction, they become a powerful tool to increase customer lifetime and generate revenue.
Why you need to constantly evaluate your behavioral segmentation
External factors will have a constant impact on your customers’ behaviors. Geopolitical turmoil, economic disruption, new technologies or simply new consumer trends can affect the efficacy of your marketing strategies.
Evaluating your behavioral segmentation on a consistent basis means you’re not surprised when more customers turn to new channels, or customer segments no longer work as effectively. Your behavioral segments will change over time, so consistently asking for customer feedback and examining your data for new behavioral patterns will help you to meet evolving customer needs and expectations.
Types of behavioral segmentation
There are many ways your customers will interact with your brand, product or service. You’ll need to understand these behavioral variables to help create a behavioral segmentation strategy that’s effective and sustainable.
AI-powered platforms can analyze all these behaviors along the customer journeys, identifying trends and patterns that will help you predict which customers are most likely to make which purchases.
The main ones are:
1. Purchasing behavior
How do customers behave on their journey to purchase?
Purchasing behavior can be segmented into four categories:
- Complex: Imagine the work that goes into making a purchasing decision to buy a new home. Customers are highly involved, research in-depth, and eventually buy something that is a one-off or infrequent purchase.
- Dissonance-reducing: Do you worry that you might regret your purchase? You’ve been highly involved in the purchasing process, but you’ve found it hard to choose between brands. Customers will seek follow-up reassurance that they made the right choice.
- Habitual buying: Every week you go to the grocery store and buy whichever products are cheapest or feature a special offer. You have no brand loyalty; this is your habit.
- Variety-seeking: You’re bored with citrus-scented shower gel, so you choose a cedarwood-scented option. The citrus one cleaned your body just fine, but you wanted variety.
2. Usage behavior
How often do customers use your product/service and how?
This behavioral segment looks at the frequency of customer interaction with your business, and the nature of the interaction (what they do while interacting, which features they use, how long they spend, etc.). This can be further segmented into heavy or light users (or even more granular), and you can update your marketing strategy to target these segments accordingly.
3. Benefits sought
Which particular benefit is a customer seeking when they decide to make a purchase?
Customers place higher value on one benefit over another when choosing a product. A classic example is toothpaste. Any toothpaste can contribute to good dental health, but customers may prefer to choose:
- Sensitivity relief
- Whitening
- Tartar control
- Cavity protection
- Gingivitis prevention
- Fresh breath confidence
- Gel or paste
- Children’s
- Whatever is cheapest
Understanding the benefits your customers are seeking is a key part of behavioral segmentation, as it directly affects the purchasing process.
4. Occasion or timing-based
Which special occasions do customers buy for?
These include universal and personal occasions:
- Universal occasions: Such as Thanksgiving, Halloween, or winter holidays are some examples of when people are more likely to make specific, seasonal purchases.
- Recurring personal occasions: Annual events such as birthdays, anniversaries, or vacations, as well as quarterly, monthly or daily purchases, like newspapers or coffee.
- Rare-personal occasions: Things like weddings, baby showers, college graduations (being mindful that these are harder to predict).
5. Customer journey stage
Where is the customer currently along their journey?
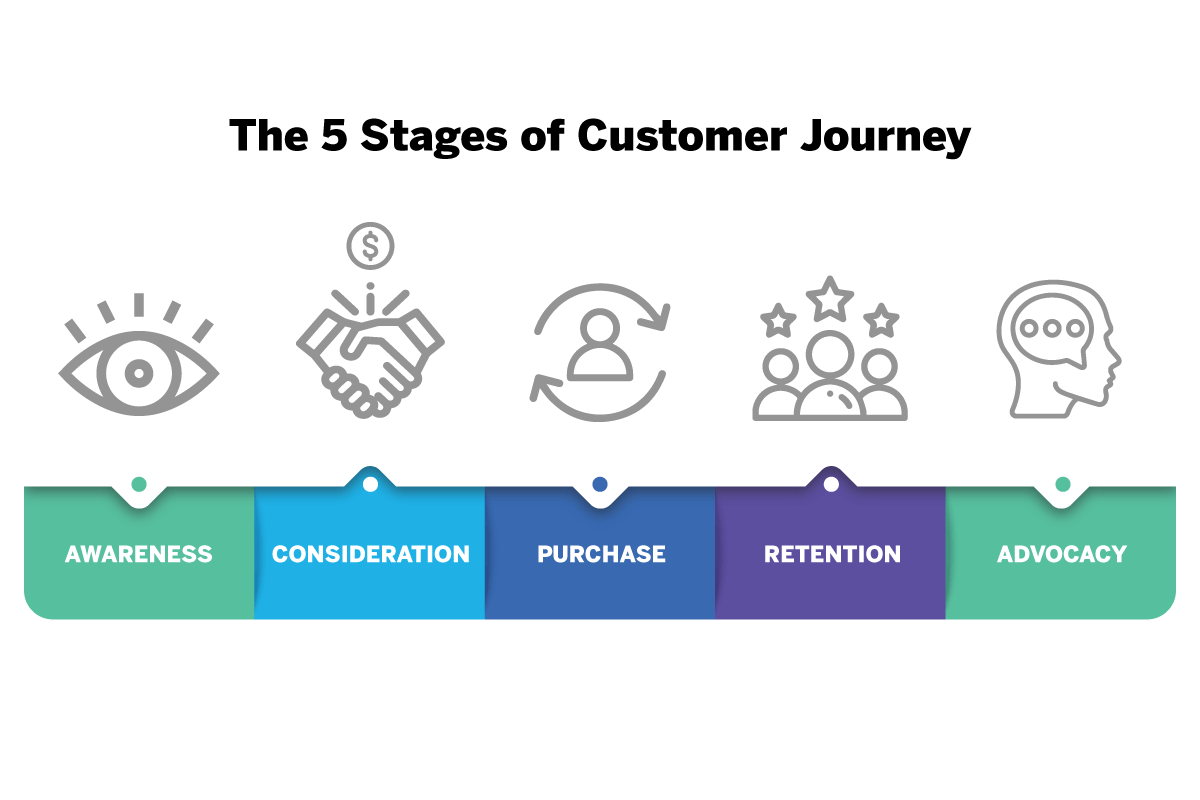
The customer journey is, at its most basic, the process that considers when a customer becomes aware of a product to the point where they’ve bought the item and are telling others about it. There are five touchpoints along the customer journey:
- Awareness (Advertising, radio & TV, PR campaign)
- Consideration (reviews, blogs, direct mail, email marketing campaigns, social ads)
- Purchase (website, store, contact center)
- Retention (loyalty program, community, newsletters)
- Advocacy (word of mouth, social media, reviews)
Behavioral segmentation using the customer journey stage will reveal any pain points or sticking places where the customer cannot complete their journey. For example, at Purchase, the store may habitually be out of stock, highlighting a problem with supply.
6. Customer satisfaction
How happy are your customers?
Customers’ needs, wants, and experiences change in real-time as they progress through their purchase journey. What drives customer satisfaction at one point won’t necessarily be true at all points in time.The traditional Net Promoter Score alone doesn’t really cut it anymore, as it doesn’t reach all customers and there’s too much unmonitored time that passes between surveys. Real-time behavioral data is a much more accurate and reliable measure of true customer satisfaction.
7. Customer loyalty
Which customers are most loyal?
Your most loyal customers are your most valuable, as they spend the most time connected with your brand. They are:
- Cheaper to retain
- Have the highest customer lifetime value
- Are your best brand advocates, contributing to brand equity
Once you’ve performed customer loyalty behavioral segmentation, you need to find ways to maximize these customers’ value and bring in more like them. Behavioral segmentation gives you insights into their needs so you can retain them with special VIP privileges and rewards that will strengthen the customer relationship.
8. Interests
What are your customers interested in?
If you can continually pique your individual customers’ interests, they’ll keep coming back for more. Keeping customers engaged makes it easier to increase their usage of your product or service, keep them loyal on your platform or in your store, and sell them other products.
Netflix and Spotify are masters of this type of behavioral segmentation, keeping subscribers watching and listening with suggested content and recommendations based on previous behavioral interest.
9. Customer engagement level
Who are your most (and least) engaged customers?
Different companies will have different interpretations of ‘engagement’ but, generally speaking, when customers have positive experiences with your brand and are willing to interact with you regularly, there’s a good chance this will lead to profitable outcomes.
10. User status
How do people use your business?
This is another way to use behavioral segmentation to sort different customers by how much they use your business. These can include, but are not limited to:
- Non-users
- Prospects
- ‘Freemium’ users (consumers who use a free product but pay for add-ons or in-app purchases)
- First-timers
- Regulars
- Defectors (previous customers who’ve switched to a competitor)
11. Spending Habits
How do customers spend their money with you?
These tell you how customers spend their money, as well as where and when they generally buy. This segment may include:
- Buying online vs. in-store
- Buying with a store credit card vs. a regular credit card
- Using coupons vs. never using coupons
- Visiting during sales vs. non-sale times
12. Brand Interactions
How do customers engage across all your branded channels?
This kind of behavioral segmentation tracks all interactions with your brand, both online and off, and demonstrates how engaged a customer is with your brand. Think of the Disney brand, which covers movies, merchandising, dedicated stores, websites, theme parks, vacations.
Interactions include:
- Frequency of store visits
- Frequency of website visits
- Web pages visited
- Interactions with your social media
- Content viewed on social media
- Frequency of purchase
- Previous purchases
Behavioral segmentation: examples of how to utilize segment data
Once your brand has evaluated data through behavioral segmentation, you can then use this information to more effectively target your customers.
Here are some examples of what you can do with the information you’ve sourced through behavioral segmentation:
Use your most loyal customers’ information to repeat success
To illustrate this point, imagine your company is a technology brand. Your customer loyalty segmentation has unveiled which of your target audience spend the most with your business. As you discover through your customer research, it’s often because your product provides a high-quality solution to a particular tech problem, and once they purchase your solution, they often come back for more of your offering.
Your marketing efforts might have previously focused on occasion-based purchasing behavior typical for tech companies, such as Black Friday deals, but perhaps ignored creating useful resources for solving this specific issue.
By developing blog posts, FAQs and other helpful resources aimed at customers having this problem, you can better introduce your brand to them and bring them into your customer journey. As you’ve pinpointed that customers having this issue are most likely to buy from you again once they’ve tried your solution, you’re able to get the most ROI out of this marketing strategy.
Retarget customers to encourage wanted behaviors
Now, picture your brand as a cosmetics company, sending perfume to customers. Aiming your marketing strategies at new customers based on demographic and psychographic data has proven useful, but your brand struggles to build customer lifetime value.
Using retargeting in your advertising and marketing, you can sell more products to the same customers you already have, increasing your ROI. Approximately 97% of visitors who visit your website once don’t return—which means you have to attract them back with offers that appeal.
Behavioral segmentation allows you to see what drives customer purchases, and retarget accordingly. You find that customers who have bought from you before are more likely to buy citrus-based products, so you can retarget those customers with cosmetic products in a similar scent profile. You also time your marketing strategy so that it coincides with the average repurchase time for your loyal customers, ensuring that when customers run out of their perfume, they’re reminded to come back for more.
Use behavioral segmentation to move customers along the sales journey
In this example, you run a SaaS brand that has a freemium and a paid app. You’d like more customers to go through the buying process for the paid version, rather than staying on the freemium model of your product. They’re stuck in the consideration phase of the sales journey – and you’d like to move them into the conversion stage.
By examining the behavioral data of your different customers, you’re better able to see the pain points that your product solves and the benefits sought from each type of customer. Sending them in-app upgrade messages that mention the solution you provide—offering a more in-depth model, for example—that are relevant to each segment helps you to drive more conversions and therefore more upgrades.
Three case studies of behavior segmentation
Here are a few examples of businesses that are successfully employing behavioral segmentation and connecting with customers in a more meaningful way.
Case study 1: Olay discovers new product line opportunities

Olay, the US skincare brand, has a global customer base of young and older women. The brand used artificial intelligence in their mobile-friendly tool, Skin Advisor, which asked potential customers about their skin, their skincare routine, and what they wanted.
By collecting their answers, the team at Olay were able to:
- Understand their target market’s usage behavior and whether current products fit the customer needs
- Upsell products to the customers, based on their answers
- Build trust and increase knowledge by providing advice on their skin’s profile
Based on the results, Olay introduced fragrance-free products and Retinol24, a retinol-based product, which increased revenue. This is a great example of a business who was able to influence future customer behaviors with insights unlocked by customer data.
Case study 2: Thirdlove unlocks the key to purchasing decisions

Thirdlove is an American company producing and selling bras, underwear, loungewear, and nightwear. They wanted to help women find the right bra for their shape and size so they created the FitFinder tool. This tool asks a number of questions regarding how often they purchase bras, what sizes are most in-demand, and the body types of its target market.
While the customer was able to find the right information to help them make the best buying decision, the tool also helped the company. By looking at the data and using behavioral segmentation, the company was able to see that the tool was a key channel towards customer purchases: they were more likely to purchase, return and spend more, so they invested more into its development..
Case study 3: Netflix develops loyal customers with bespoke recommendations

This well-known entertainment streaming service brings TV series and movies to customers in a personalized way. They do this by using AI in an agile way, providing custom recommendations to the user, based on their previous viewing history.
Combining this usage data with AI algorithms means that predictions on behavior can be made and then tested, based on what’s served up to the user in their recommendations lists. The AI program learns from the results and continues to tailor information to the user’s profile.
The amount of data collected from all users means that Netflix can see how users consume the service and where they have trouble. This gives them the right insights to be able to update and improve their user experiences, create happier customers, and provide the highest lifetime value.
How to use behavioral segmentation to help your business
Automated brand experience management programs allow you to segment target customers, identify and develop your value proposition, conduct brand research, and personalize your communications. You can then track every behavioral brand metric that matters to your business, from awareness to loyalty and advocacy, picking up and resolving all the pain points as you go.
You will understand your customers better so you can enhance the experience of existing ones, while also connecting with new ones.
Free eBook: How to drive profits with customer segmentation