Customers expect not only a high-quality digital experience; they also expect to be treated as individuals. Their online experience must be personalized, relevant, and tailored to their wants, needs and interests. And where customers have high expectations, it follows that they have low tolerance for a below-par experience.
Now, more than ever, customers will abandon a purchase or a brand with a single click if they’re not happy, and move onto another brand that seamlessly delivers what they want. A recent study from the XM Institute asked large organizations to evaluate the quality of the experiences they deliver across different channels. Less than 30% rated any of their digital experiences as “good” or “very good”.
Modern customers are digital kangaroos, able to hop from brand to brand and product to product, on any device. Therefore, it’s essential to ensure that your brand’s path to purchase is as easy as possible, to stop them from hopping off to a competitor.
How do you do this? With digital customer journey mapping.
Free course: Customer journey management & improvement
What is a digital customer journey?
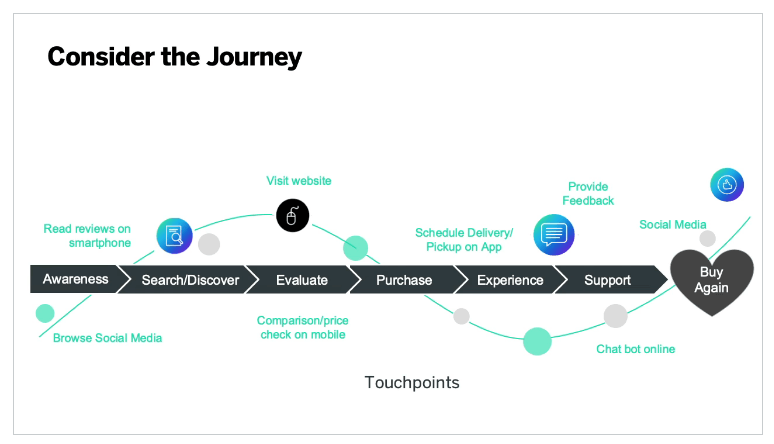
This is the path to purchase and retention – from first noticing the product to buying and using it. The journey combines all the touchpoints (i.e. points of interaction with your business) a customer has, and collects consumer data, transaction information, cross-device browsing history, and customer service interactions. There are five stages in the digital customer journey:
- Awareness: this is the point at which a customer notices your product. Awareness can come from a multitude of channels: social media and word of mouth from friends, influencers and brand advocates, search engine suggestions, adverts, marketing emails, blogs, SMS, apps, loyalty programs, and affiliate marketing.
- Consideration: A customer likes what they’ve seen, so they start to think about and research the product. They’ll visit your website, engage with a chatbot, sign up for free trials, demos, webinars, look at discounts, and check online reviews and testimonials.
- Purchase: To buy online, customers will create an account (or log into their existing one), fill their shopping cart, may be upsold or cross-sold, apply discounts, choose an electronic payment option, check out, and leave a review about the purchase.
- Experience: This is how well the order is fulfilled, and includes: shipping and delivery, tracking, online help center, support content (FAQs, instructions and assembly guides), chatbots and assisted chat, guarantees, follow-up emails and social media interactions.
- Loyalty: Loyalty programs, personalized rewards, newsletters, and social media interaction are all well and good. But creating an emotional connection with the customer, and ensuring they receive the value they expect from the brand is the new approach to loyalty: is the product good quality? Did the customer receive good support?
What exactly is a digital customer journey map?
When you map out the digital journey graphically, including all the devices, and touchpoints your customer interacts with, you’ll understand how they make decisions, connect and interact with your brand. You can also identify and rectify any pain points that make the customer experience less than seamless.
What are the benefits of customer journey mapping?
- You’ll walk in your customers’ (virtual) shoes: Employees sometimes find it difficult to empathize or understand the customer’s perspective. They may try to second guess what customers are feeling, rather than experiencing the journey themselves. By collecting feedback at touchpoints along the journey, the customer can express how they are feeling (frustrated? Happy? Disappointed? Cared for?) and employees can jump in to solve issues and make the customer experience smoother and more enjoyable.
- The whole company will work together: All too often, organizations work in silos: not only communication silos (when different teams don’t speak to each other) but also system and data silos that hold customer information that’s specific only to that part of the journey. It’s the lack of a 360 view of the customer and seamless sharing of insight that creates this fragmented experience. With a customer journey map and centralized customer information, everyone, across all departments, knows where they fit in and what their role is in delivering a seamless experience.
- You’ll inform your content marketing and content creation: Customers buy more if your content is relevant and targeted to them. Your customer journey map will help you build a full 360° picture of your customers: demographics, behavior, and psychographics, so you can target new and returning buyers.
- You’ll be able to predict customer behavior: Not only will journey mapping give you valuable insight into customers’ wants, needs, feelings, actions and aspirations, you’ll also be able to use the data to predict and influence how customers will behave.
- You’ll be able to identify gaps: when you map out each stage of the journey, and then map out your existing processes, you can not only uncover gaps, but also identify what your highest value journey touchpoints are. Without mapping, you could be focusing on optimizing touchpoints that are not really that influential, while missing a more important point.
Creating your digital customer journey map
The first thing to understand is that you have no control over a customer’s journey. A customer will go where they like, on whichever device or platform they choose, negotiating the touchpoints to achieve their goal of a satisfactory purchase. Your role is to build an omnichannel framework that anticipates where they are going to go and supports their goal.
- Base it on your sales funnel: You will probably have the basis for your digital customer journey already – your online sales funnel (awareness, interest, decision, action). Use this as a guideline to define how many touchpoints your customers have, and how each interaction funnels into the next.
- Put your customer hat on: Walk through all the stages of your sales funnel as a customer would, noting the touchpoints. What social media would they interact with? Does your website have the right information? How easy is your booking process? How helpful are the after sales people? Is the loyalty scheme attractive? Would you be happy to recommend your own product?
- Customize your touchpoints: You know which social media platform attracts most customers, how to respond to reviews so your business demonstrates it cares about customers, how your purchase process works, how good your aftersales team is, and how you reward loyal customers. These are the touchpoints that are specific to your company. When you bolt them onto your customer journey map and collect feedback about each of them, you’ll be able to see if they are performing as well as you think they are.
- Create personas: As companies scale, it becomes harder and harder to keep track of individual customers. This is where personas come in: these are fictitious customer types based on real customers, using demographic and psychographic profiles that include age, gender, socioeconomic background, lifestyle, interests, opinions, likes, dislikes, and attitudes. Each persona travels along their customer journey in a slightly different way, enabling a company to recognize the differences and cater to every type of customer.
- Use customer journey mapping software: Customer journey solutions are now so sophisticated that they can give real-time visualizations of your customers moving towards purchase and beyond, capturing their online interactions with your brand. AI-enabled software will flag any touchpoint where customers are struggling and highlight any places where they drop out. Not only can you jump in and fix the problems, you can also measure the impact that improving the customer experience at those points has on the company’s bottom line.
Data you can collect with digital customer journey mapping
These are just some of the types of data you can collect along your digital customer journey. When you feed all these into a single platform for analysis, you’ll be able to see how they relate to each other, and where they have knock-on effects.
- Web-browsing data: Every time someone clicks onto your website, you can track their activity on the site and see how they are interacting with your brand. You can also see what devices they are using to access your site.
- Mobile app data: If a customer is using your mobile app, they already have a degree of loyalty. Mobile apps yield more customer information from profiles, sign-ins, and location.
- Sales data: You can track a customer’s purchase history and shopping habits over time. Do they buy immediately, leave items in their shopping cart, or abandon their cart periodically? Don’t forget sales that didn’t happen – finding out why not is valuable for understanding what needs to improve.
- Advertising data: Who has clicked through to your site from an advertisement? This data will give you information about customers who are just starting out on their journey with you. You can marry advertising data with sales data to test the effectiveness of your ad campaigns.
- Loyalty data: Your best customers are usually those in your loyalty program. By analyzing who they are and how they use your brand, you’ll be able to target people just like them.
- Survey data: Want to know what customers think of your brand? Ask them. Sending surveys at touchpoints along the customer journey can give you quality information about what’s working and what’s not.
- Social media listening: Increasingly, customers interact with brands through social media. Understanding the nature of this interaction can help develop your social, as well as general marketing strategies.
- Aftersales data: Information from your customer services department can reveal a wide range of issues: product quality, delivery reliability, areas that need product support. How customers are treated after they’ve made a purchase is pivotal to whether they become loyal, or not.
What about B2B digital customer journey mapping?
Whether you’re selling B2C or B2B, the main principles of journey mapping are the same. After all, although you are trading with companies, you are still selling to people within those companies – there are just more of them, and your feedback processes will need to be a little different.
When you map B2B journeys, you need to bear the following in mind:
- More types of people are involved in a B2B journey than a B2C one: Therefore, you’ll need to create more customer personas. For example, if you’re supplying an online finance platform, you will have to deal with the CIO, executives, managers, tech personnel and the call center assistants. All these people are your customers, segmented by persona.
- B2B customers are more valuable: Building business relationships can take years of investment, and if you lose a business customer, you might lose a lot of revenue as a result. You’ll need to prioritize and segment your customer personas by business value: the CIO has more purchasing power than a single call center assistant, for example.
- B2B customer feedback is different: Because much B2B is built on personal interaction and recommendation, business people often know each other. It’s more acceptable to pick up the phone and talk through a problem than send out a generic survey. Your feedback techniques will have to be much more personalized to each of your B2B customers, so that they feel heard, and still special.
An example of a customer journey map template
The brands that thrive in this new reality are those that understand what customers want in digital and take action to deliver the experiences they expect. Here’s a customer journey template for you to start mapping out your digital journey.
To learn more about customer journey management take a look at our free online course below:
Free course: Customer journey management & improvement